10.23.2025 / 6-minute read
Innovative Core Flipping Station Design
Overview
In the world of transformer manufacturing, the assembly of the core is a critical process that directly impacts performance, efficiency, and safety. Traditional methods for creating 3D stacked cores often rely on manual flipping and positioning—a process that is labor-intensive, imprecise, and poses significant safety risks.
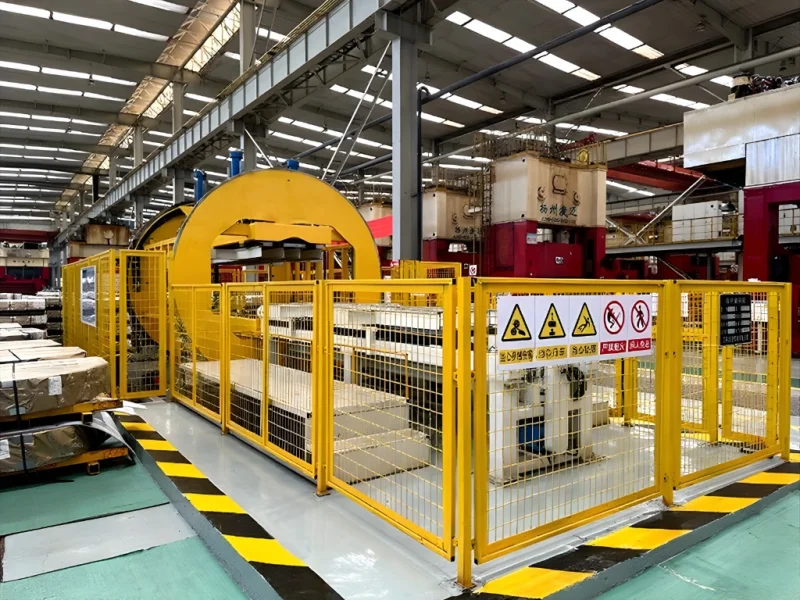
To address these challenges, we have developed a groundbreaking Transformer Core Flipping Station. This engineered solution automates the stacking and flipping process, ensuring precision, enhancing worker safety, and boosting overall productivity. Let’s delve into the technical design of this innovative equipment.
The Core Challenge in 3D Stacked Core Assembly
A 3D stacked core transformer offers superior performance, including reduced material consumption, lower losses, and higher efficiency.
However, assembling the three individual core segments into a final, unified structure is complex.
Manual handling is not only slow but also risks damaging the delicate laminated cores and endangering personnel.
Our Automated Solution
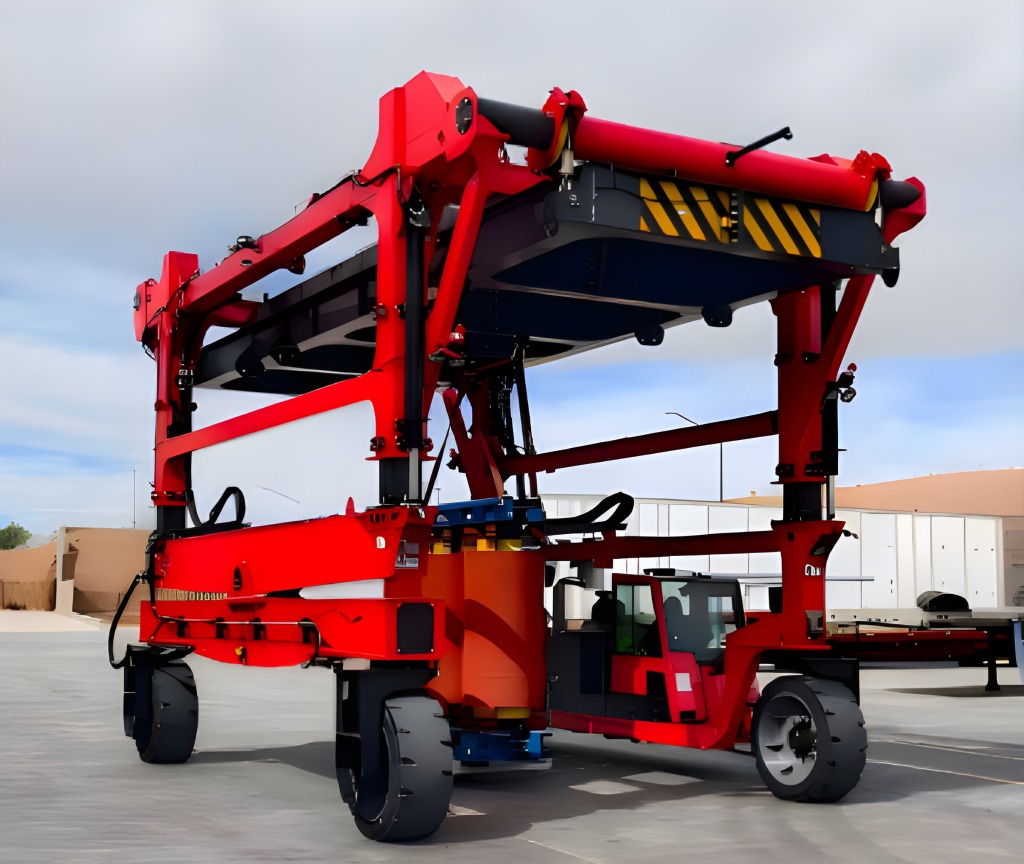
Our Core Flipping Station is engineered from the ground up to automate the entire process. The design focuses on stability, precision, and seamless integration into the production line.
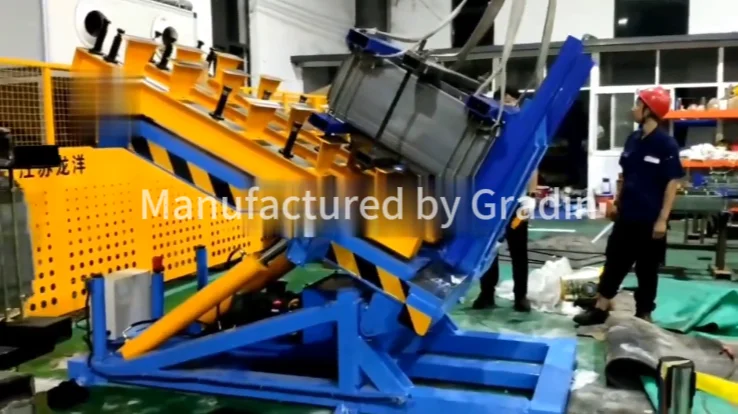
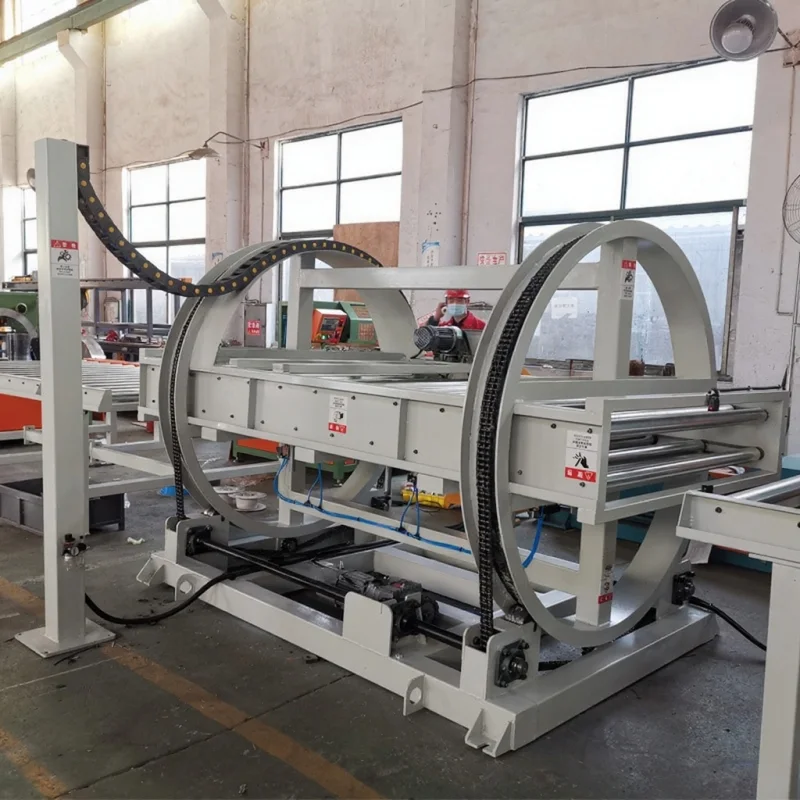
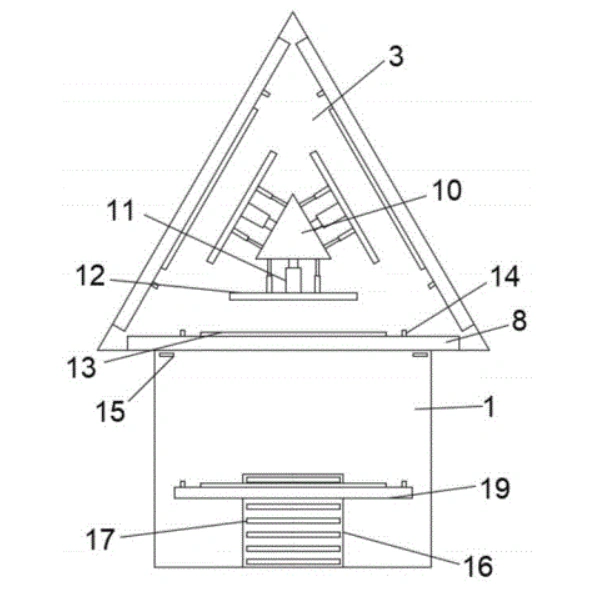
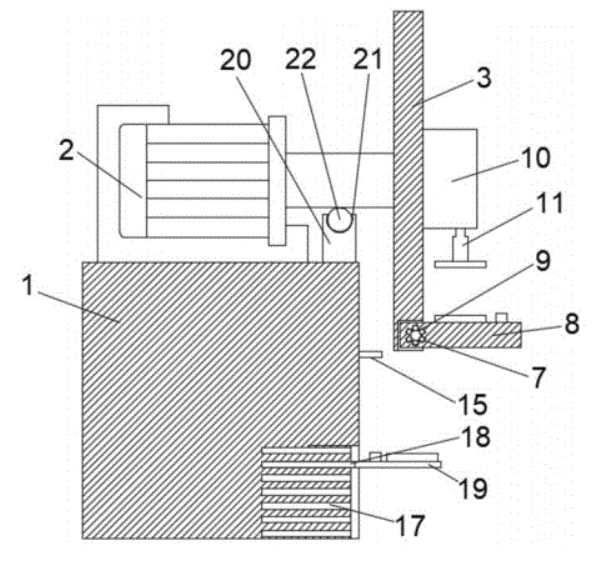
1. The Central Rotating Framework:
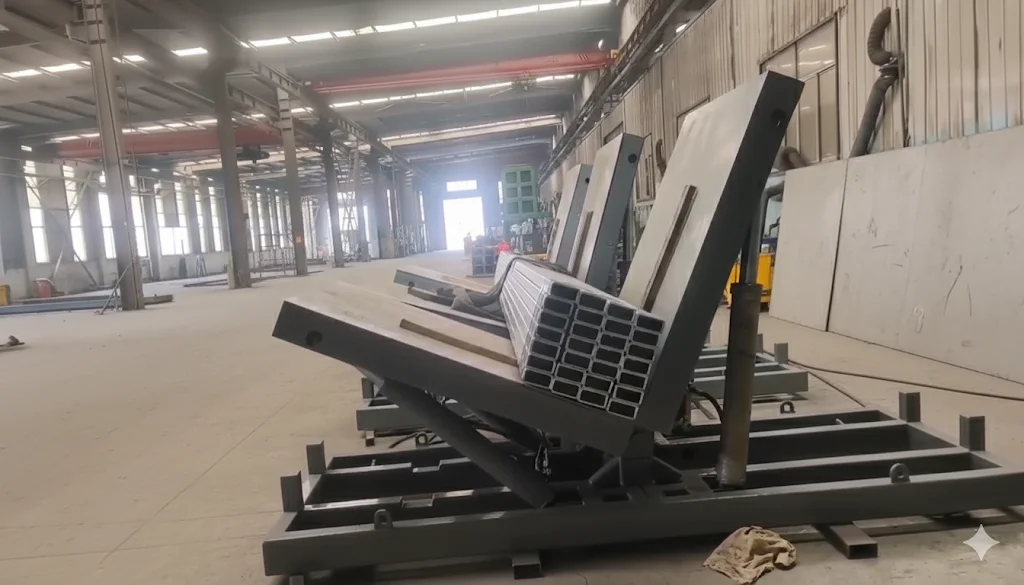
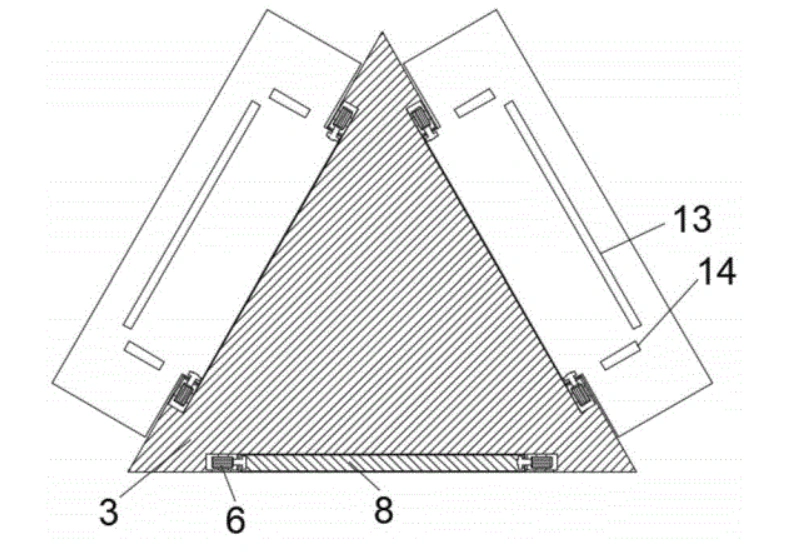
The heart of the system is a robust base supporting a first motor. This motor drives a unique triangular plate, which serves as the central hub. Each of the three sides of this plate is engineered with an installation slot to hold a support plate.
2. Automated Support Plate Flipping:
Each support plate is a workspace where operators stack silicon steel laminations to form one side of the final core. The innovation lies in the flipping mechanism:
- Second Motors & Locking Blocks: Inside the triangular plate, a second motor is housed within an installation chamber adjacent to each support plate. This motor actuates a locking block.
- Secure Engagement: The side of each support plate features a card slot. Once a core segment is stacked, the locking block extends, engaging with this slot to securely lock the plate in its horizontal position.
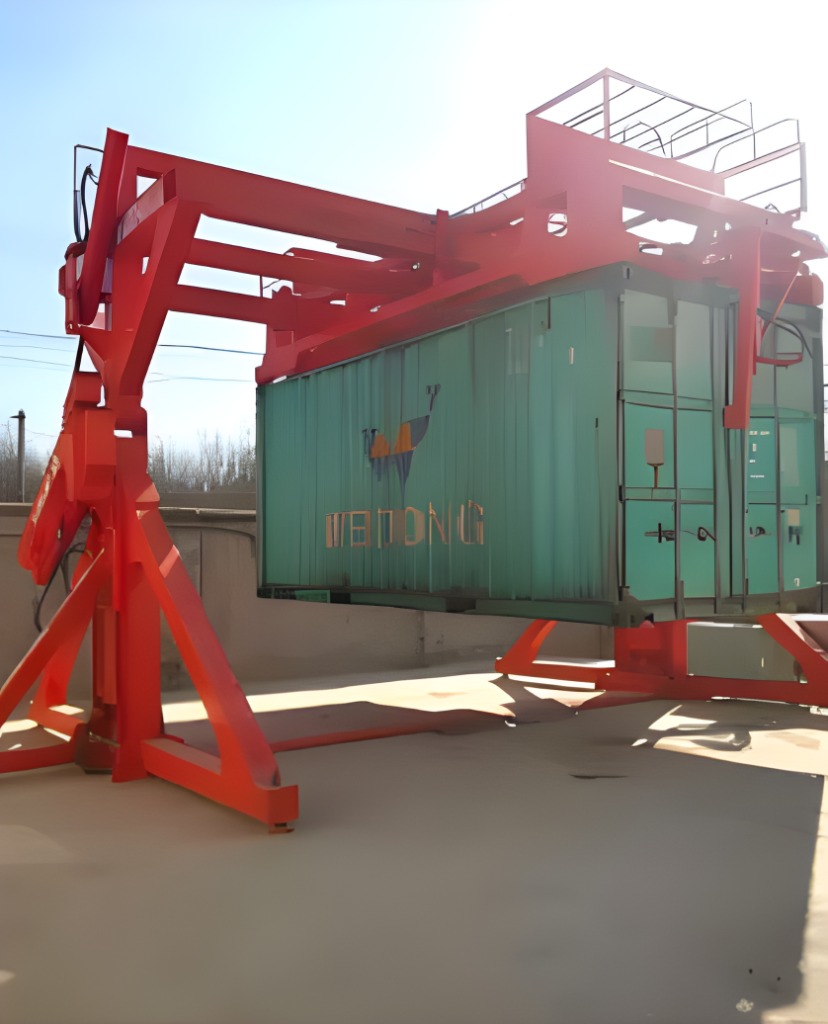
3. Precision Core Positioning & Clamping:
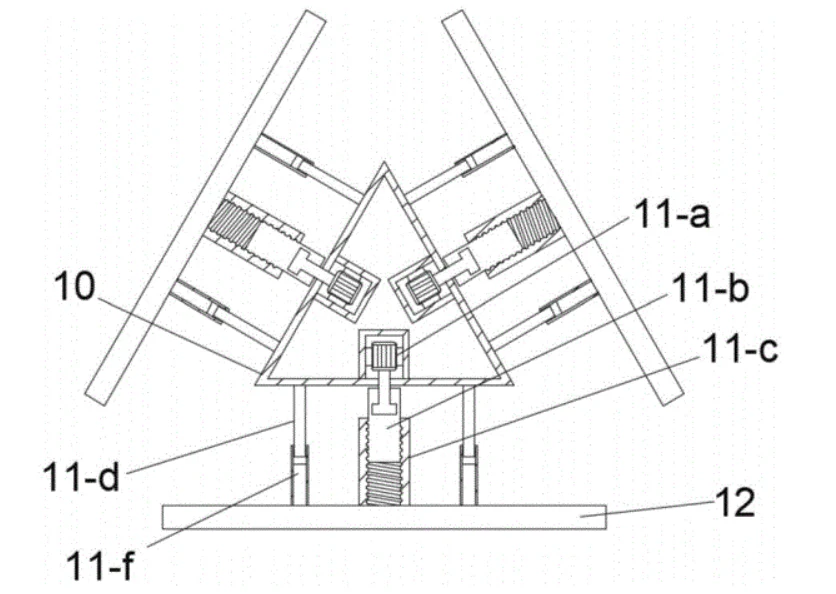
To ensure the stacked laminations are perfectly aligned and fixed during rotation, a sophisticated clamping system is mounted on the front of the triangular plate.
- A central triangular block acts as an actuator housing.
- On each of its three faces, a pressing plate is mounted via a connection device. This device, which can be a motor-driven screw mechanism or a hydraulic cylinder, drives the pressing plate forward to apply uniform pressure on the stacked core, holding it firmly in place.
Key Operational Steps
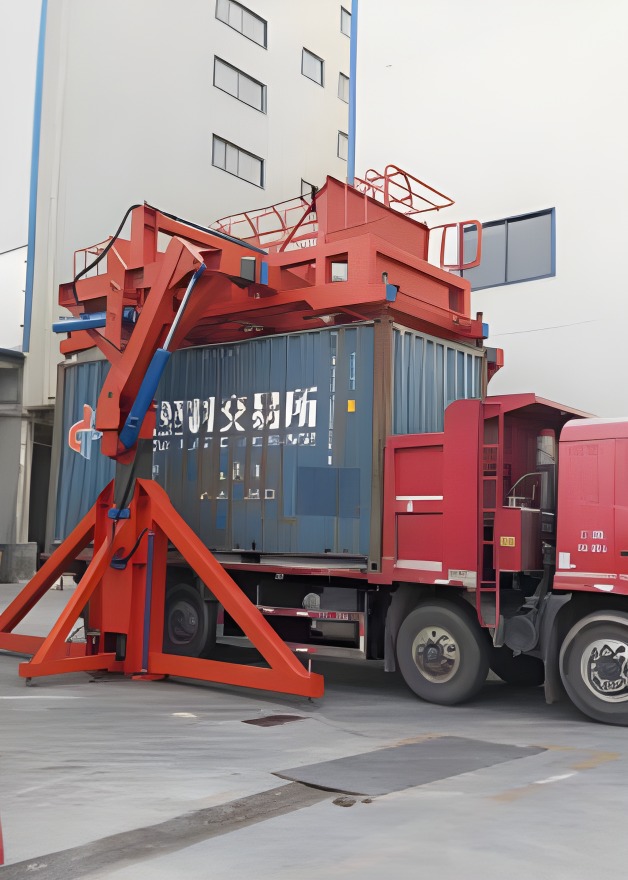
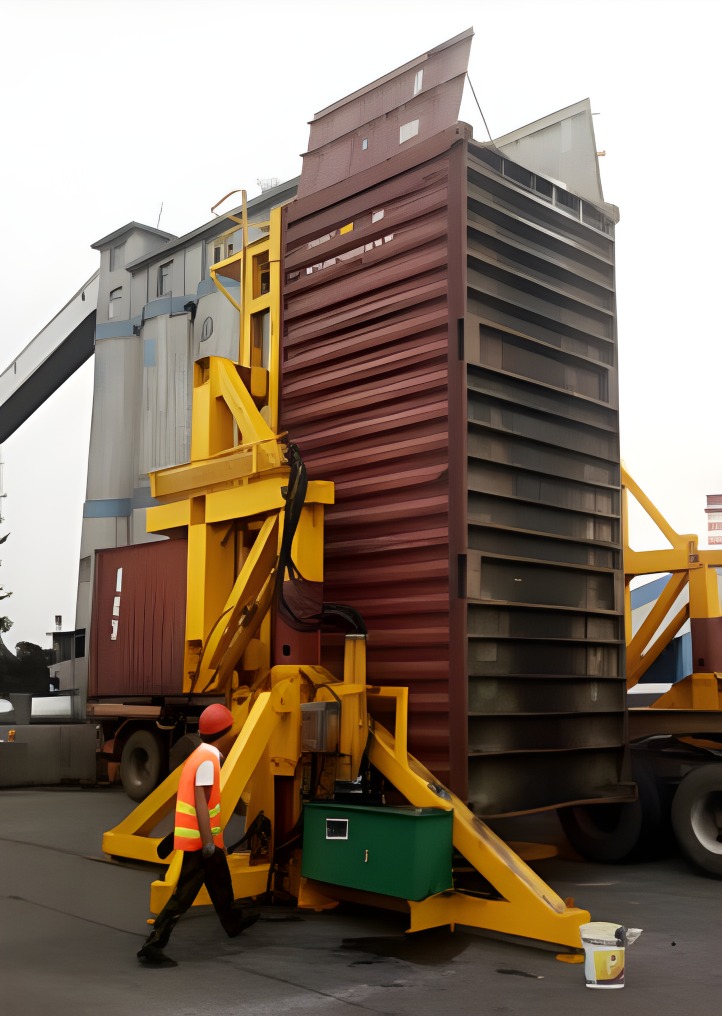
- Stacking Phase: Operators stack silicon steel laminations onto the three horizontal support plates. The plates are locked in place, and the clamping system secures the stacks.
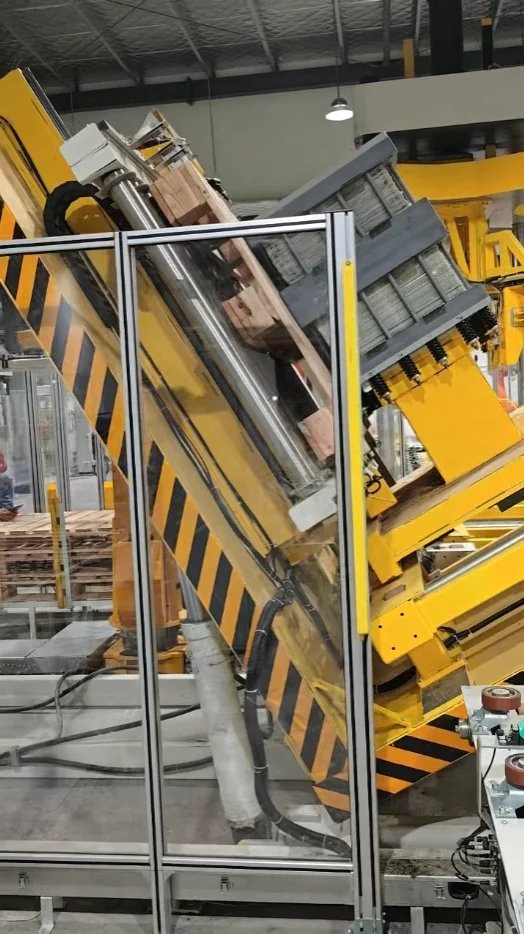
- Assembly Phase: After all three segments are stacked, the first motor rotates the triangular plate to the desired orientation. The second motors then disengage the locking blocks, allowing the support plates on the sides to be flipped vertically—either manually or via an integrated actuator—bringing the three core segments together to form the complete 3D core.
- Finalization: The assembled core is then released from the clamps and removed for the next stage of production.
Design Advantages & Technical Superiority
- Enhanced Safety: Eliminates the need for workers to manually lift and flip heavy, cumbersome core segments.
- Guaranteed Precision: The locking and clamping mechanisms prevent core deformation and misalignment during rotation, ensuring a geometrically perfect final assembly.
- Operational Efficiency: Allows for continuous stacking on multiple sides and enables rapid, automated assembly, significantly reducing cycle times.
- Robust Construction: Features like the support block with roller beads reduce friction on the main motor’s output shaft, enhancing durability and smooth operation.